
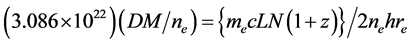
Astronomical Distance Travel Time Calculator computes the time to travel to distant parts of space at different velocities.Sun, Moon, planets, stars, Milky Way's Center and Edge, Andromeda Galaxy) This is known as ‘cosmological redshift’ (or more commonly just ‘redshift’) and is given by: for relatively nearby objects, where z is the cosmological redshift, obs is the observed wavelength and rest is the emitted/absorbed wavelength. Astronomical Distance Calculator provides the distance from the Earth to numerous astronomical bodies (e.g.Distance from absolute and apparent magnitude.Blackbody Temperature from Peak Wavelength.Wavelength Shift from Wavelength and Speed.Velocity from shift in Wavelength and Unshifted Wavelength.( 9) Several different models of dark energy were proposed so far. Relative Luminosity from Relative Temperature and Size To compare predictions of different models of dark energy with high redshift Hubble diagram we use the standard definition of the distance modulus: (z, ) 25 + 5 log dL (z, ).Relative Temperature from Relative Size and Luminosity.Relative Size from Relative Temperature and Luminosity.Mass of extra-solar planet from mass and velocity of star and velocity of planet.where emit emit is the emitted wavelength. (Image credit: Wikipedia) Redshift z z is the fraction by which the wavelength increases. Mass of extra-solar planet from mass of star, radius of star orbit and radius of exoplanet orbit 1: Absorption lines of the sun as compared with absorption lines from a distant supercluster of galaxies.(S) - size or diameter of astronomical object.Small Angle Formula Small Angle Formula α = S / D.(R) - separation distance between the two objects.The Astronomy Calculator Suite includes functions that are useful for studying astronomy and include the following: We can change te to redshift z using the relation. This formula gives the magnitude of the wavelength shift given the speed of the source relative to the observer (for speeds well below the speed of light only!). We can rearrange the distance modulus equation to solve for distance. The formula for the recession velocity of a galaxy is:Ī source of light moving toward or away from an observer will have it's spectrum shifted toward the blue (moving toward) or to the red (moving away). Red Shift is used to compute the recession velocity of a galaxy. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu. Recession Velocity (V): The calculator returns the velocity in kilometers per second. In this case, \(\Omega > 1\).The Galaxy Recession Velocity calculator computes the velocity of a galaxy away from Earth based on the redshift and the speed of light. The photonbaryon gas therefore has an equation of state that is well. Matter terms dominate: If the Universe contains enough mass to counteract its expansion and there is no dark energy, it will eventually collapse. cosmological redshift z of an object gives the ratio between the scale factors.If there is no dark energy, the Universe will continue to expand, but increasingly slowly. Otherwise you're treating H as a constant, i.e the universe is not expanding. Critical Universe: We have already discussed the case of a critical Universe, where the expansion and density terms are equal, \(\Omega = 1\), and space overall is not curved. \begingroup Then the second equation you provide is incorrect, since the expansion of the universe must be accounted for, ie.One of the major efforts in cosmology over the past several decades has been to determine the value of \(\Omega\).įrom the Friedmann equation, we can see that the interplay of the expansion of the Universe, density, and curvature lead to several possibilities for the fate of the Universe, depending on which term in the equation dominates:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
